


Basic Information & Test Pattern
JEE, or Joint Entrance Examination, is an Entrance Examination that is required to be written by those interested in pursuing Engineering. It is constituted by two Examinations: JEE Main and JEE Advanced (regarded internationally as one of the most challenging Undergraduate Admission Tests). Some 10.5 Lakh+ aspirants write this Exam each year. With Skoolmo’s Mock-Tests, one can practice, learn and score better...with ease!
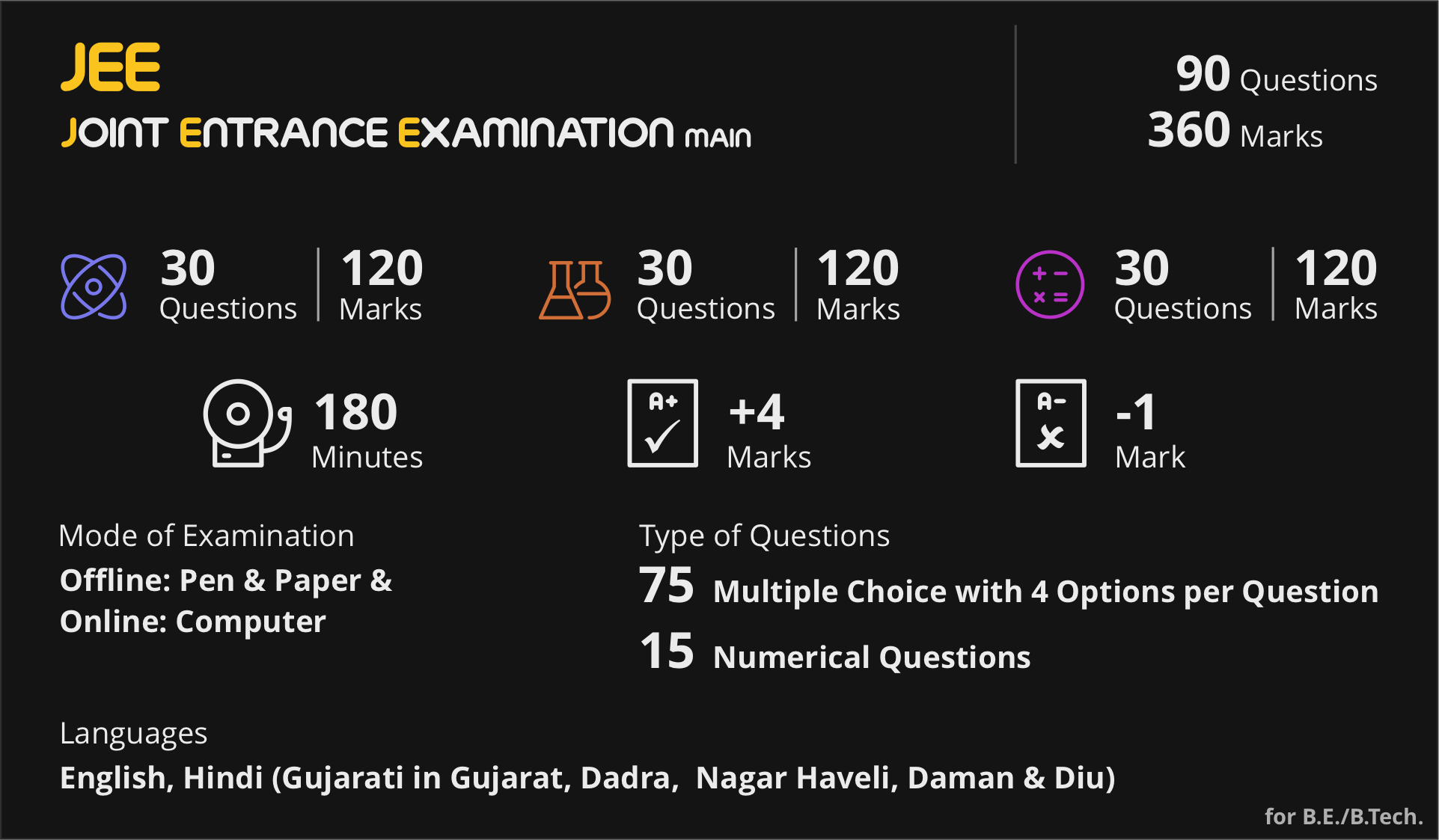
All JEE Examinations will be held in 'Computer Based Test' (CBT) Mode only, except the Drawing Test for B.Arch., which will be held in “Pen & Paper” (offline) Mode. A Candidate may appear in B.E./B.Tech., B.Arch. & B.Planning, depending upon the Course/s he/she wishes to pursue.
Important Dates
| STATUS | DATE | EVENT |
|---|---|---|
| CLOSED | 03 SEP, 2019 to 100 OCT, 2019 | Apply online on www.nta.ac.in |
| CLOSED | By 10 OCT, 2019 | Pay Fees online |
| CLOSED | 12 SEP, 2019 to 30 SEP, 2019 | Photo correction |
| CLOSED | 14 OCT, 2019 to 20 OCT, 2019 | Application correction |
| CLOSED | From 04 NOV 2019 to 08 NOV 2019 | Application [J & K Candidates] |
| CLOSED | By 06 DEC, 2019 | Admit Card available |
| CLOSED | By 06 JAN, 2020 | Examination (between) |
| CLOSED | 31 JAN, 2020 | Results |
| CLOSED | 07 FEB, 2020 to 07 MAR, 2020 | Apply online on www.nta.ac.in |
| CLOSED | By 07 MAR, 2020 | Pay Fees online |
| POSTPONED | By 16 MAR, 2020 | Admit Card available |
| POSTPONED | 03 APR, 2020 to 09 APR, 2020 | Examination (between) *POSTPONED* |
| POSTPONED | 30 APR, 2020 | Results *POSTPONED* |
Eligibility
Examination Centres
List of Examination Centres for JEE:
Examination Centres Outside India
| CITY | CODE |
|---|---|
| Bahrain | ZZ01 |
| Colombo | ZZ02 |
| Doha | ZZ03 |
| Dubai | ZZ04 |
| Kathmandu | ZZ05 |
| Muscat | ZZ06 |
| Riyadh | ZZ07 |
| Sharjah | ZZ08 |
| Singapore | ZZ09 |
Syllabus
The National Testing Agency (NTA) recommends the following Syllabus for the Joint Entrance Examination (JEE-Main), for Admission to Indian Institutes of Technology (IIT) and other Engineering Colleges across India. Each Module has been broken down into important Topics, to make for easy Studying.
Syllabus for Paper-1 [B.E./B.TECH.]
Physics: Chapter Weightage
| Topics | Questions | Marks | Weightage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physics & Measurement | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Kinematics | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Laws of motion | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Circular Motion | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Work, Energy & Power | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Rotational Motion | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Centre of Mass | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Gravitation | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Elasticity | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Thermodynamics | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Kinetic Theory of Gases | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| SHM | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Sound Waves | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Electrostatics | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Current Electricity | 3 | 12 | 10.00% |
| Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Alternating Current | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Electromagnetic Waves | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Optics | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Atoms & nuclei | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Semiconductors | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Communication System | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Total | 30 | 120 | 100% |
Chemistry: Chapter Weightage
| Topics | Questions | Marks | Weightage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transition Elements & Coordination Chemistry | 3 | 12 | 10% |
| Periodic Table & Representative Elements | 3 | 12 | 10% |
| Thermodynamics & Gaseous State | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Atomic Structure | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Chemical Bonding | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Chemical & Ionic Equilibrium | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Solid State & Surface Chemistry | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Nuclear Chemistry & Environment | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Mole Concept | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Redox Reaction | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Electrochemistry | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Chemical Kinetics | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Solution & Colligative Properties | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| General Organic Chemistry | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Stereochemistry | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Hydrocarbon | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Alkyl Halides | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Carboxylic Acid & their Derivatives | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Carbohydrates, Amino Acid & Polymers | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Aromatic Compounds | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Total | 30 | 120 | 100% |
Mathematics: Chapter Weightage
| Topics | Questions | Marks | Weightage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sets, Relations & Functions | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Complex Numbers | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Quadratic Equation | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Matrices & Determinants | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Permutations & Combinations | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Binominal Theorem | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Sequences & Series | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Limit, Continuity & Differentiability | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Maxima & Minima | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Tangent & Normal | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Indefinite & Definite Integrals | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Area Under the Curve | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Differential Equations | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Straight Line | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Parabola | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Ellipse | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Hyperbola | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| 3-D | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Vector | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Statistics & Probability | 2 | 8 | 6.67% |
| Trigonometric Equation | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Height & Distance | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Mathematical Reasoning | 1 | 4 | 3.33% |
| Total | 30 | 120 | 100% |